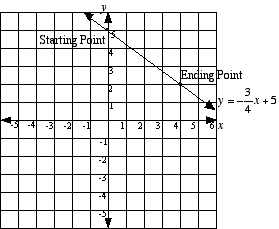
Notice: the y-intercept is at 5, so the starting point is 5 on the y-axis. Then you will go down 3 units and run 4 units to get to the endpoint. You can now draw the line that goes through these two points.
There are two forms of linear functions that we will be working with.
The first form is called the slope-intercept form. The reason that it is called the slope-intercept form is that you will need to know what the slope of the line is and also the y-intercept. This is also known as the rate of change and the initial condition.
Here is the slope-intercept form: y = mx + b. The letter m represents the slope (rate of change) and the b represents the y-intercept (initial condition). Let's look at an example of this.
What is the equation of the line that contains the slope of 3 (which is 3/1) and a y-intercept of 12. The equation that we would write to represent this information is y = 3x + 12.
Look at it the other way. What if you are given the equation y = -3/4x + 5. Can you identify the slope and the y-intercept? The slope is -3/4 and the y-intercept is 5.
Can you draw the graph of the equation y = -3/4x + 5?

What about the other form of a line? The point-slope form uses any ordered pair that is on the line, but also needs the slope.
The point-slope form for a line is y - y1 = m(x - x1). The slope is again represented by the letter m, and whatever ordered pair you have will get substituted by (x1, y1).
For example, if you know that the point (-3, 2) is on the line with a slope of -1/2, you can write the equation of that line. The equation will be y - 2 = -1/2(x - -3), remember that when you have a minus with a negative, it becomes a plus, so the equations becomes y - 2 = -1/2(x + 3). Then to make this equation into y = form, you will need to add 2 to both sides. The final equation becomes y = -1/2(x +3) + 2.
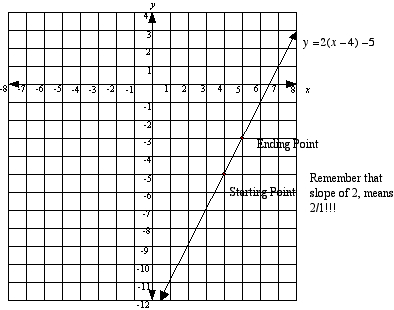
Find the slope and point that was used to make the equation y = 2(x - 4) - 5. The slope is the easy part, which is 2. The point on the line is going to be (4, -5). Let us draw a graph of this line.
Assignment: Make a graph of each linear function on your own graph paper.
1. y = -3/2(x + 6) +1 2. y = -4x +7 3. y - 6 = (x - 3)
4. y + 4 = 2/3(x - 5) 5. y = -1/2x - 4 6. y = 2/7x - 6
7. y - 2 = -1(x + 4) 8. y - 0 = 3(x + 0) 9. y = 6x + 3